ANALYSIS
[QVAPOR: deviation from 0]
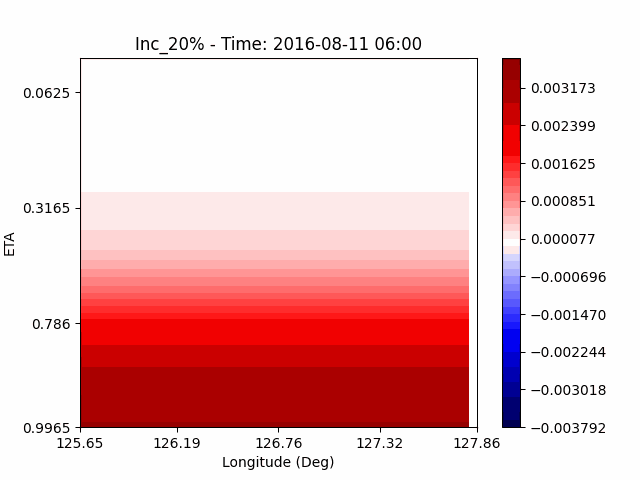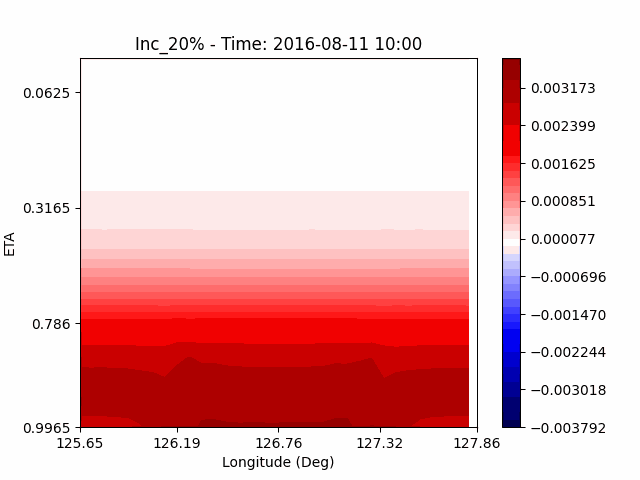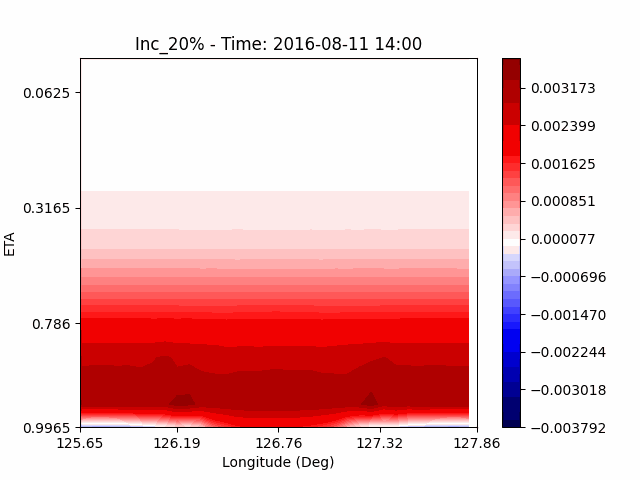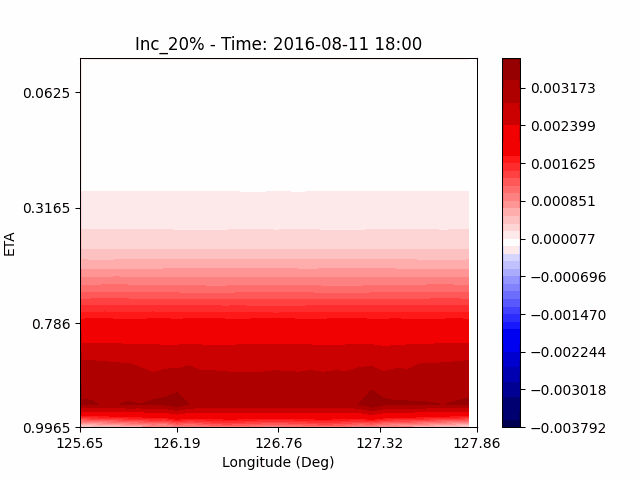
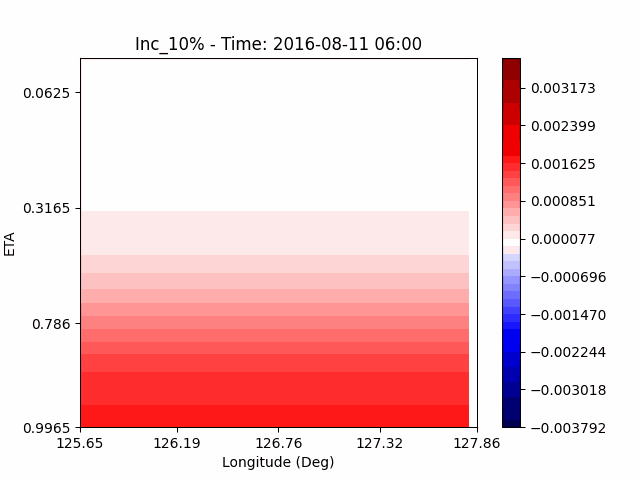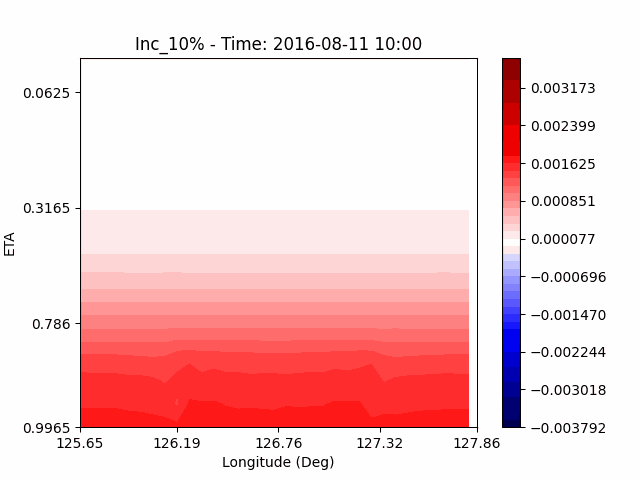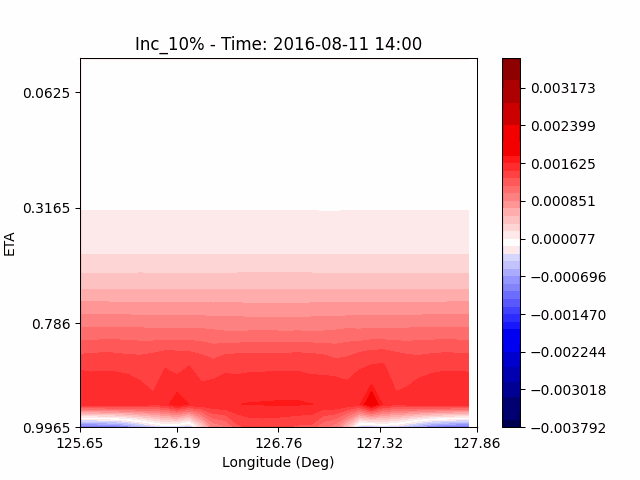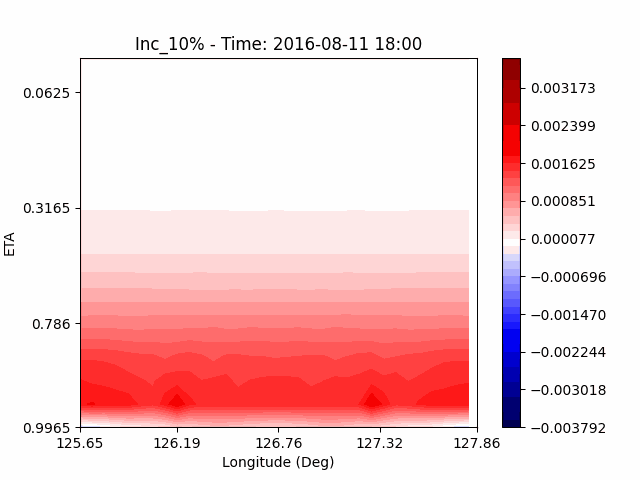
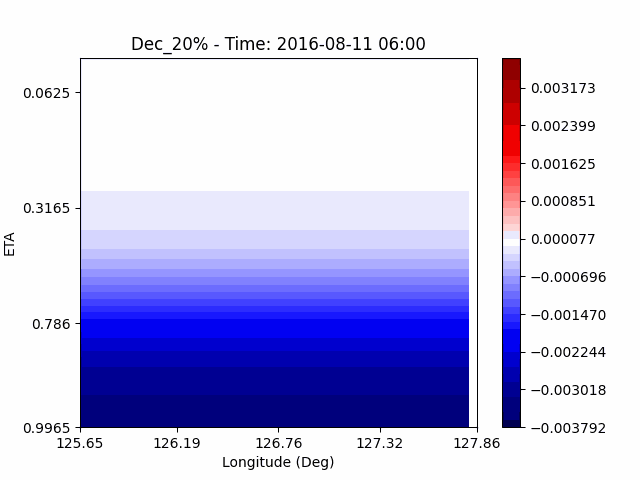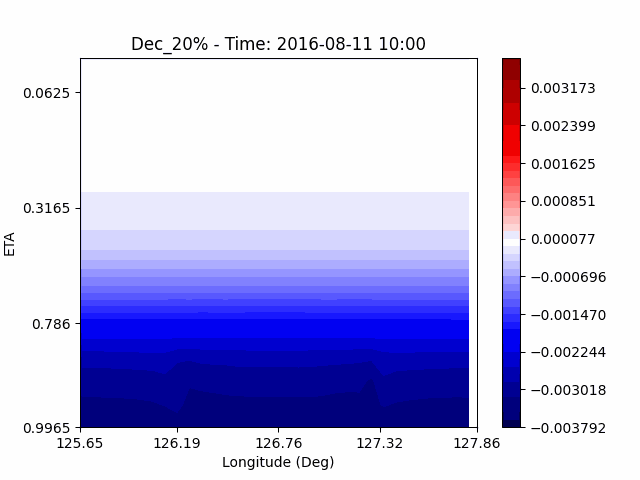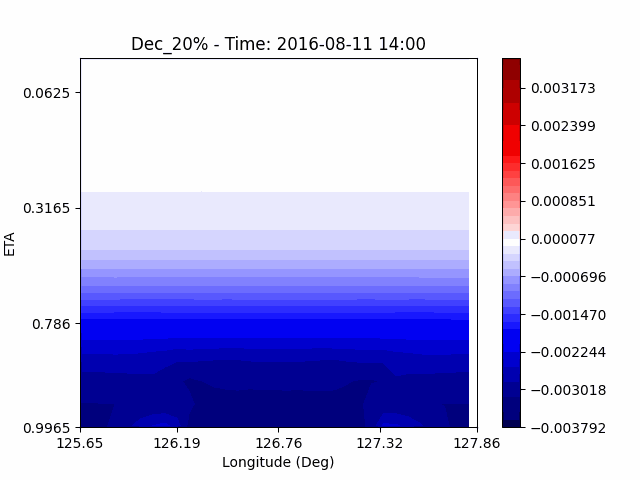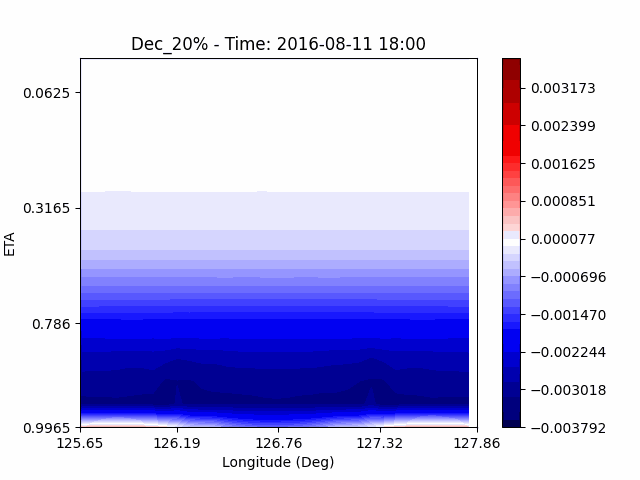

As a result of checking the deviation of QVAPOR from the control, it was confirmed that in the experiment that increased the amount of water vapor, the amount of water vapor decreased partially near the surface, and in the experiment that decreased the amount of water vapor increased partially near the surface, especially for pasture area, not the urban area.
[T: deviation from 0]

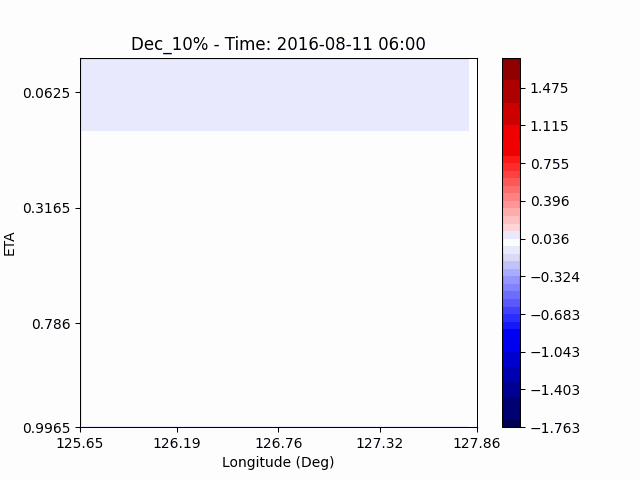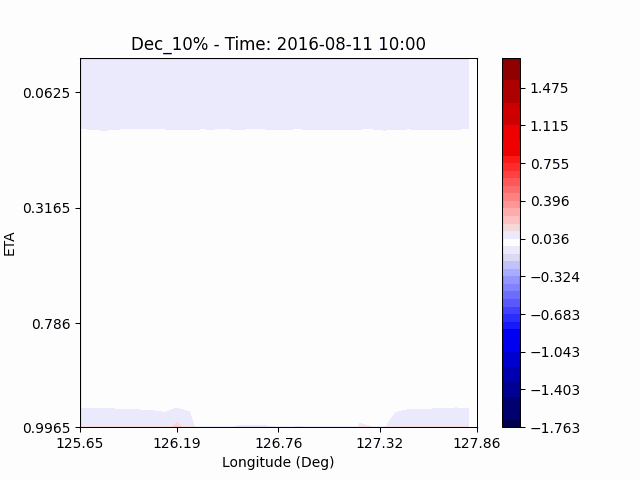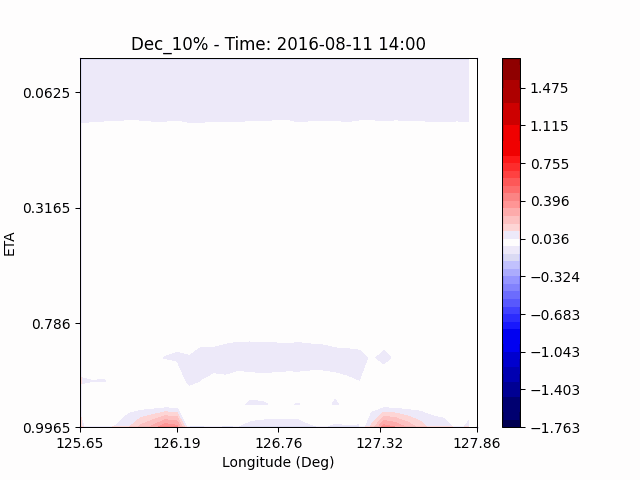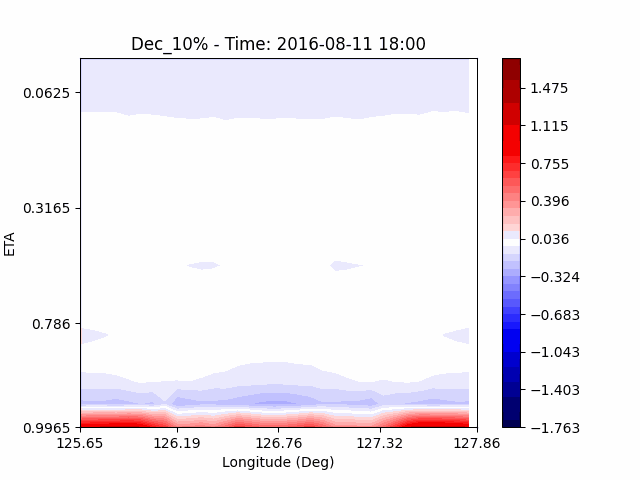
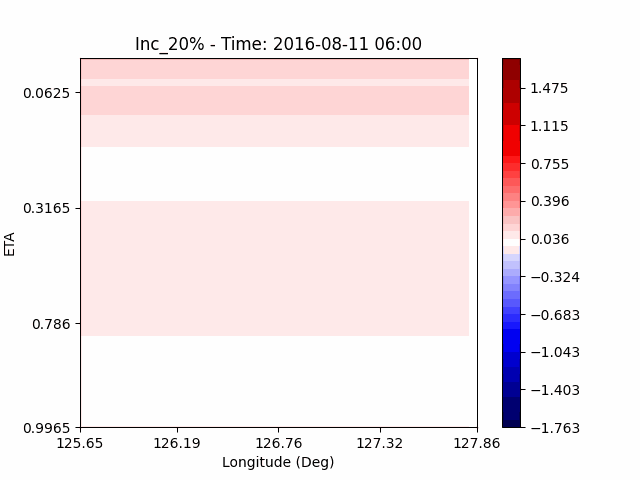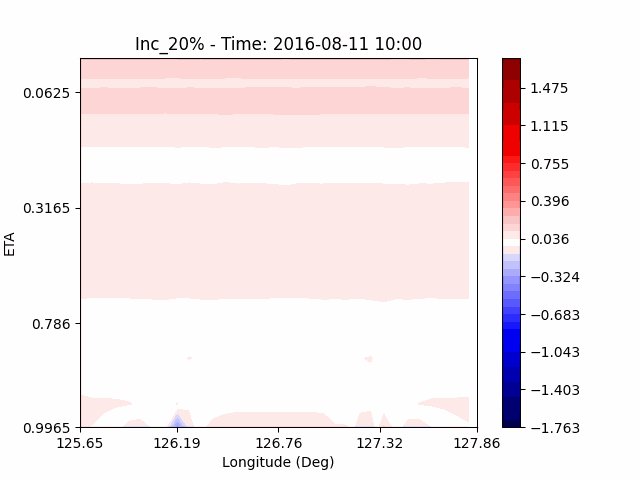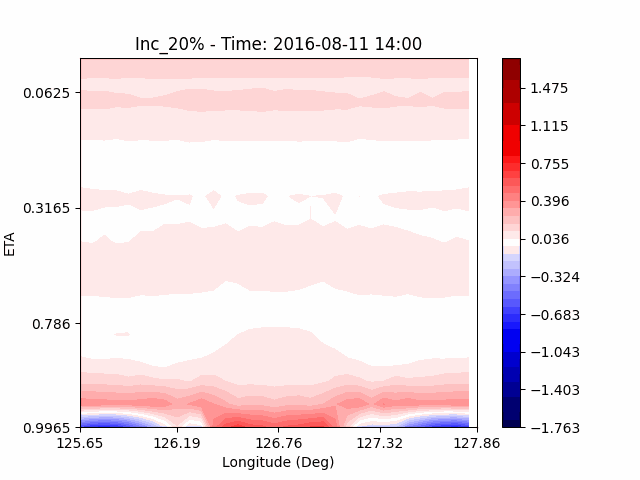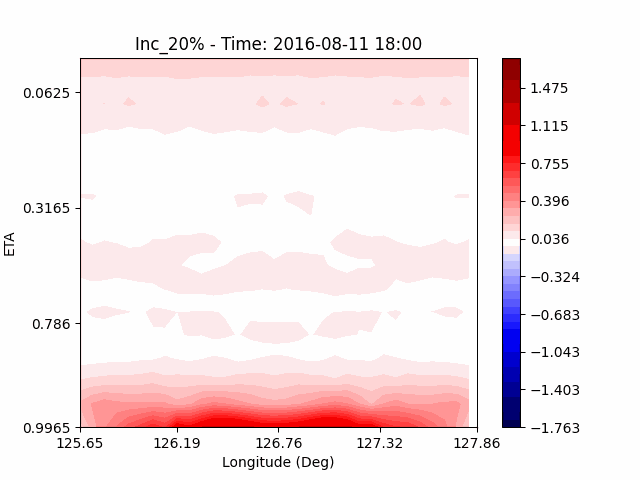
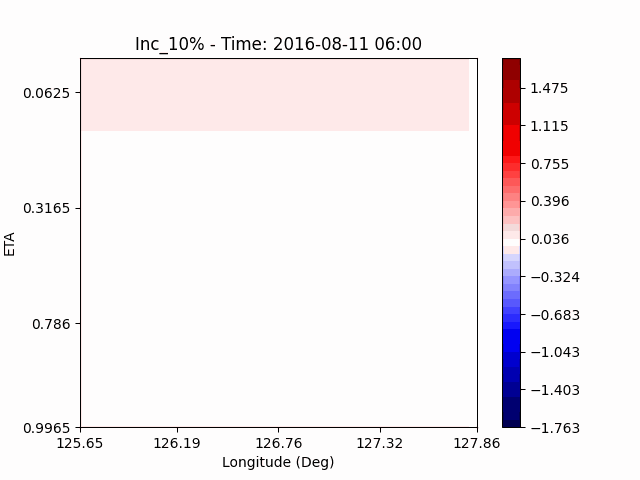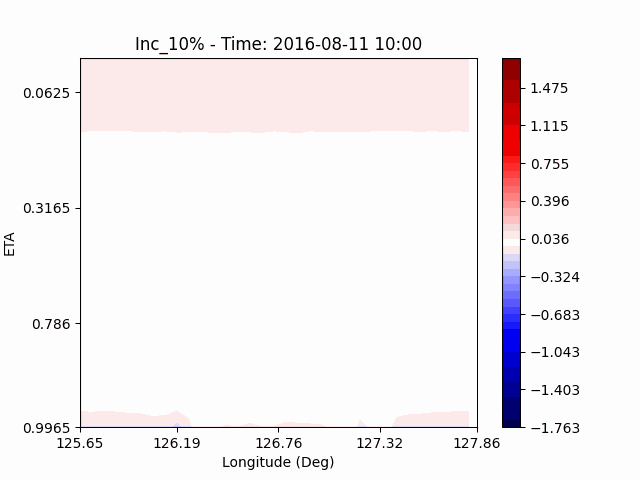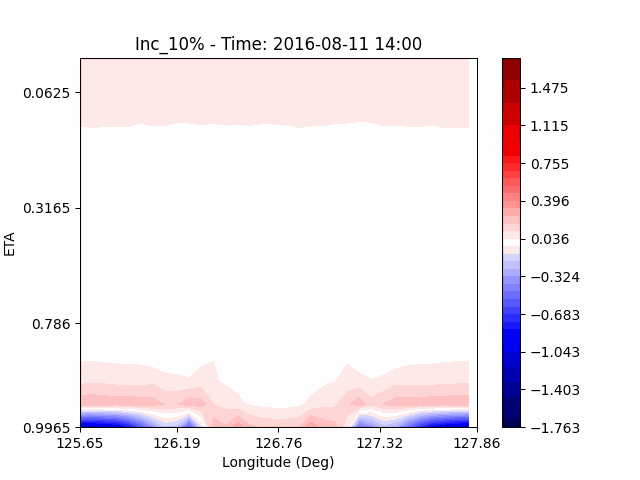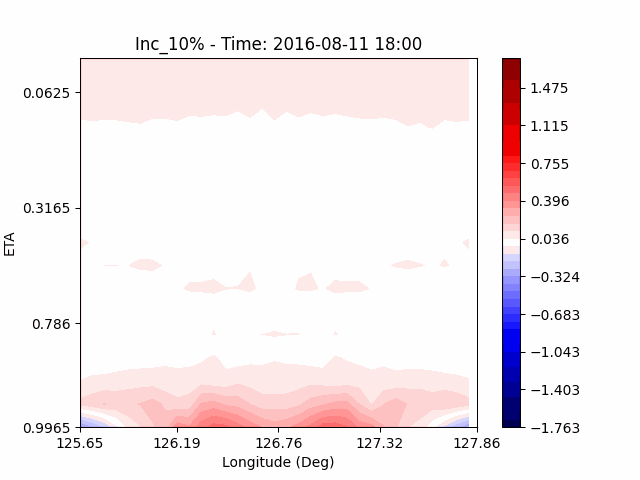
In the case of temperature, it can be seen that the heat island effect was enhanced in the center of the city in an experiment that increased water vapor, which is consistent with previous studies (Kim and Choi 2012). And, like the pattern of QVAPOR, in experiments that increased the amount of water vapor, a temporary decrease in temperature in the pasture area occurs, and in experiments that decreased, a temporary increase in temperature in the pasture area occurs.
This phenomenon is thought to be caused by water vapor feedback from pasture and the atmosphere. If there is a lot of water vapor, less evaporation can occur in pasture containing relatively little water vapor, alleviating heat stress caused by the heat island phenomenon (Chen 2014), and in the opposite case, evaporation from pasture can increase heat stress caused by the heat island phenomenon.
[UHI index]
The UHI index shows larger values with an increase in water vapor content, indicating that the urban heat island effect is more pronounced when there is a higher atmospheric water vapor.
Initially, there is not a significant difference as the air in both urban and rural areas starts heating simultaneously. However, as time progresses, areas with higher water vapor content in the urban region (red and orange) cool down more slowly compared to areas with lower water vapor content (blue and purple), leading to a pronounced difference in Index values. This is attributed to the difference in cooling rates due to the specific heat of water vapor.

[U-wind]
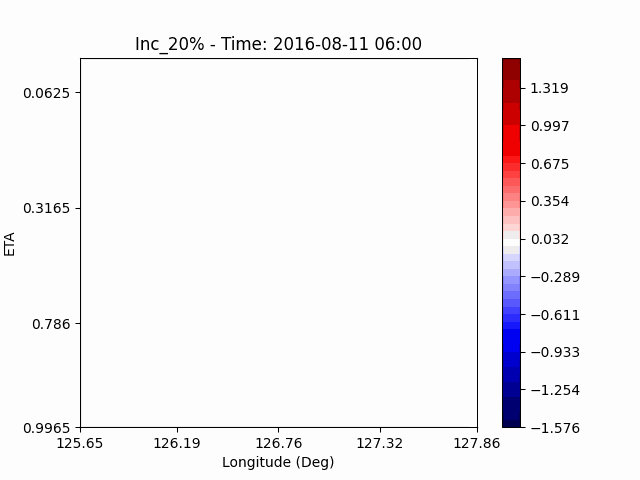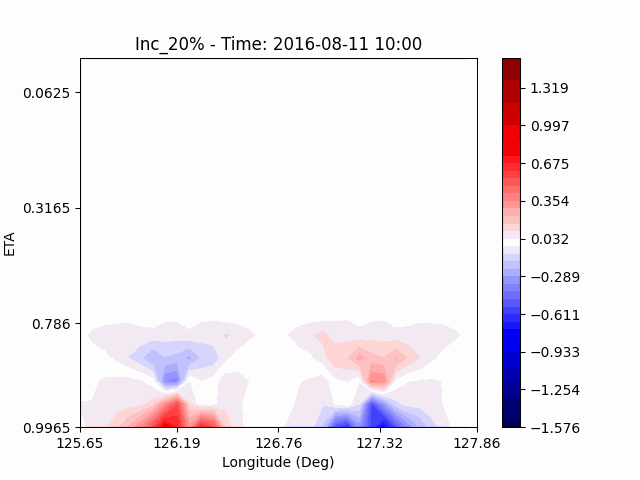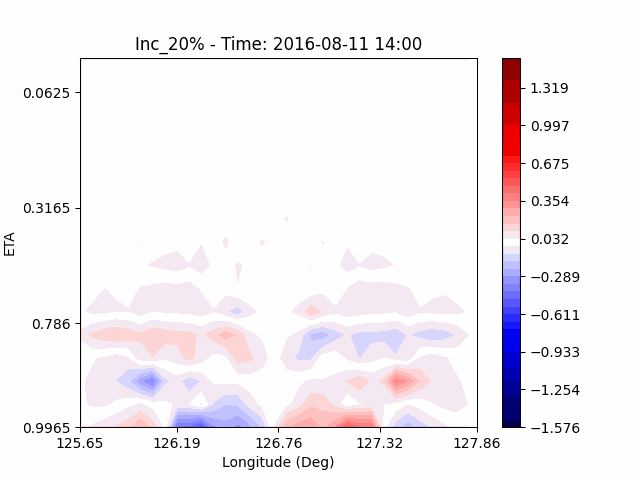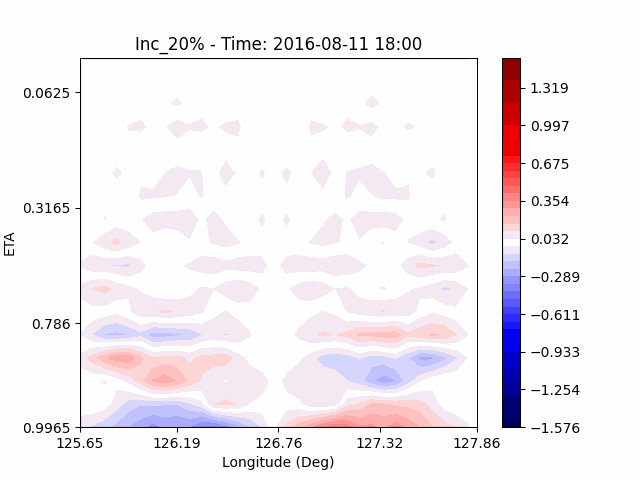
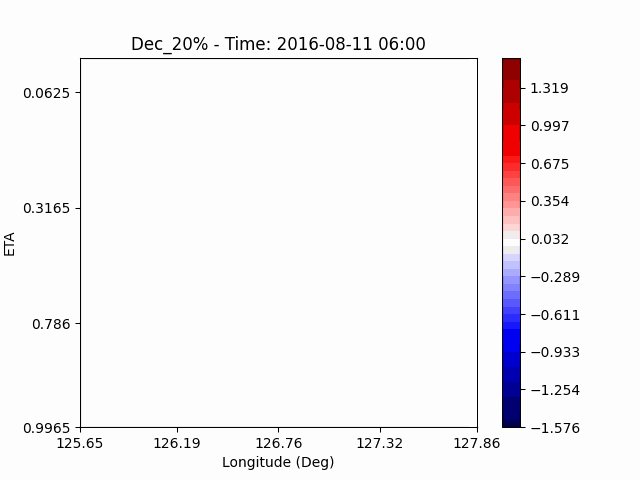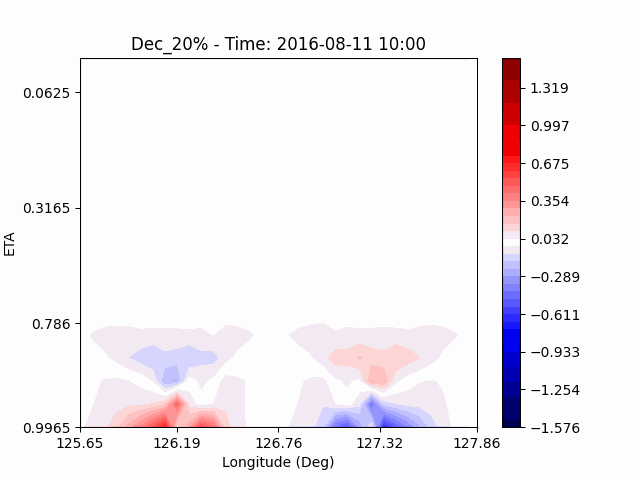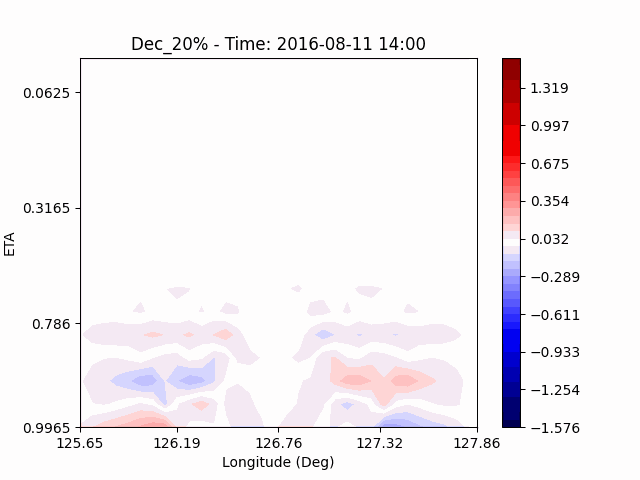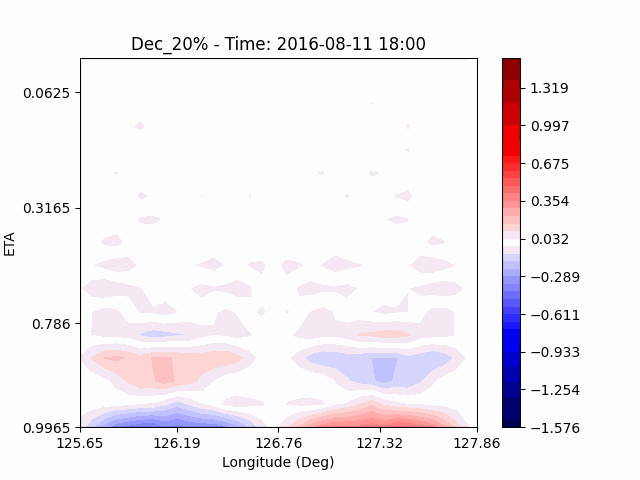
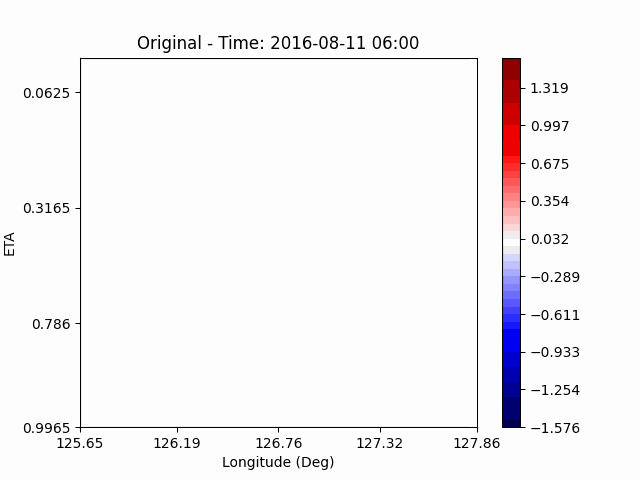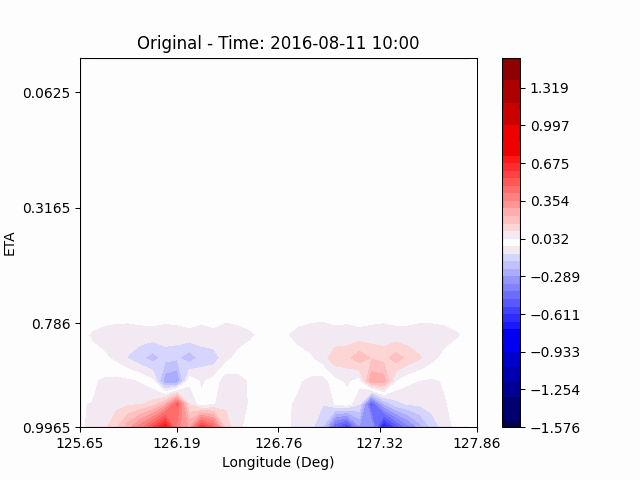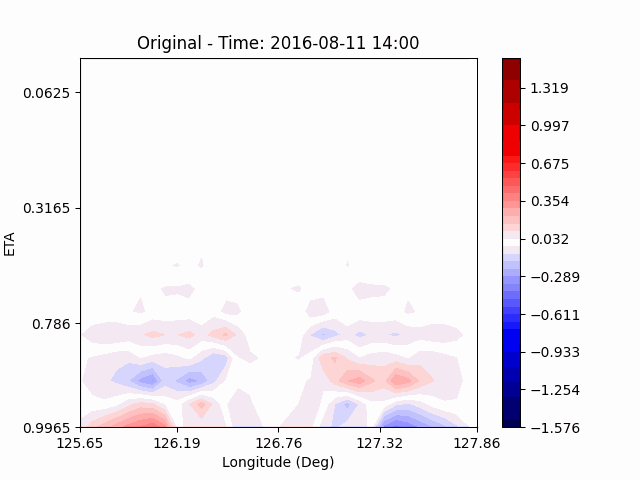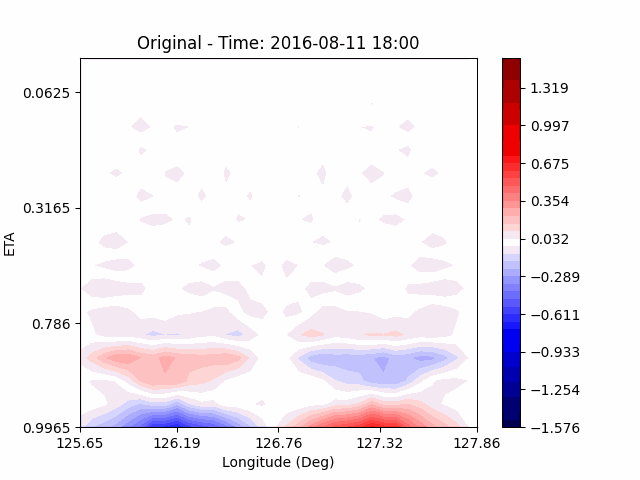

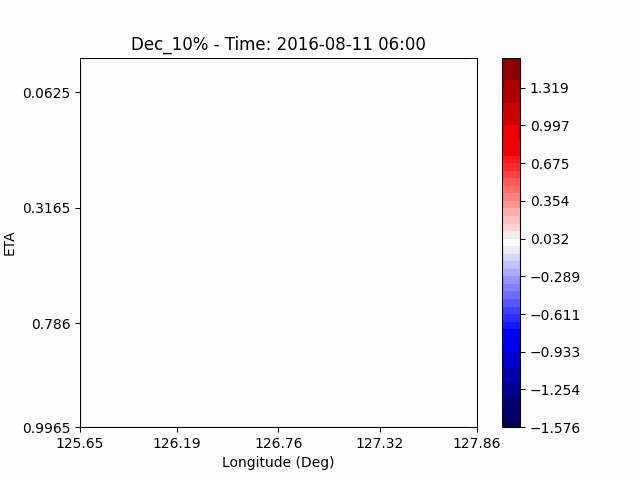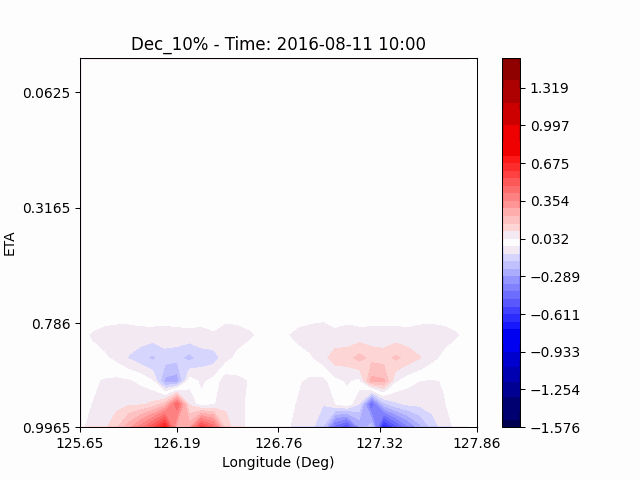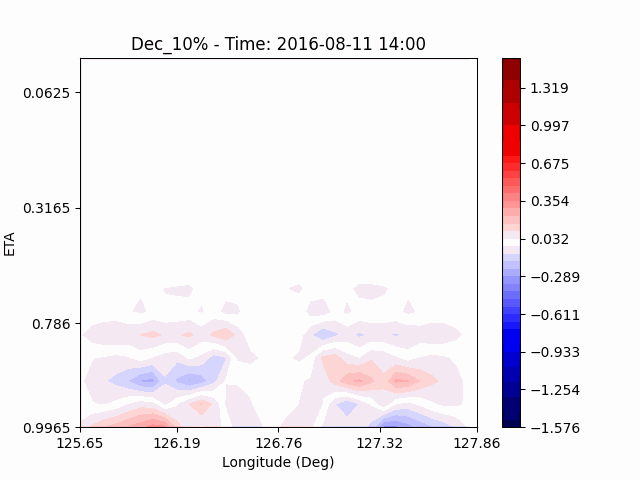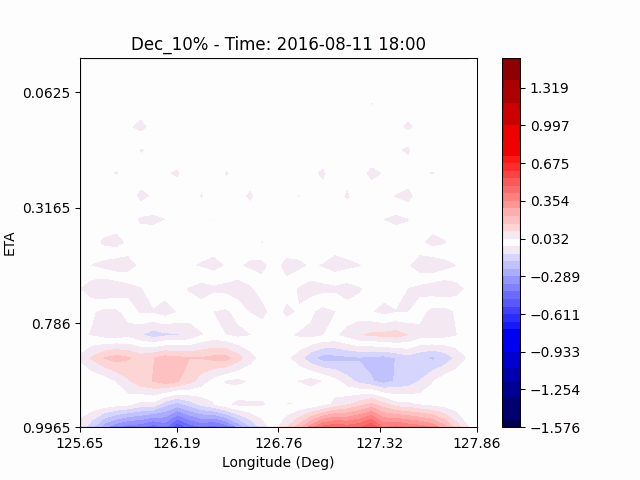
The u-directional wind shows that below the height of convection, the wind of the lower layer converges to the center of the city, and the upper layer wind blow outward from the center. After a certain period of time, we could see that the wind direction of the lower and upper layers was reversed. Here, we could confirm that if the air contains a lot of water vapor, the amount of heat that water vapor can contain increases, and the intensity of convection on heat dome increases.
[W-wind]
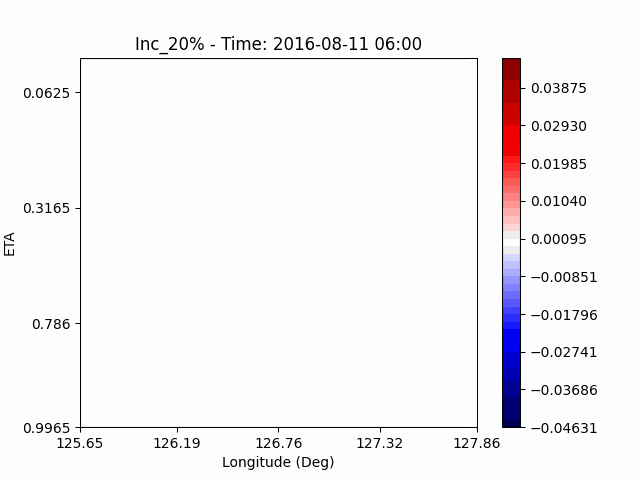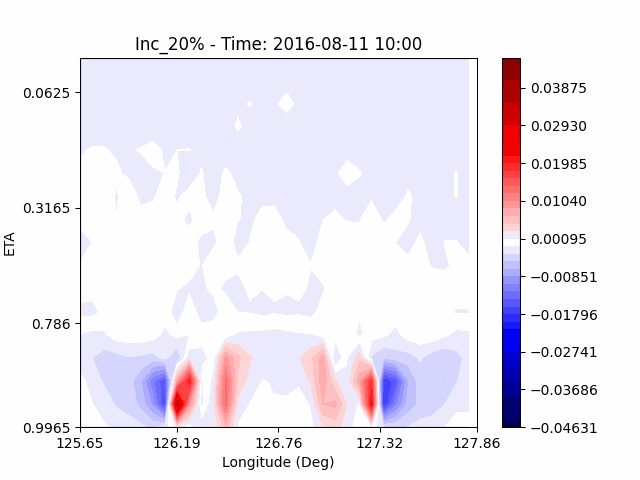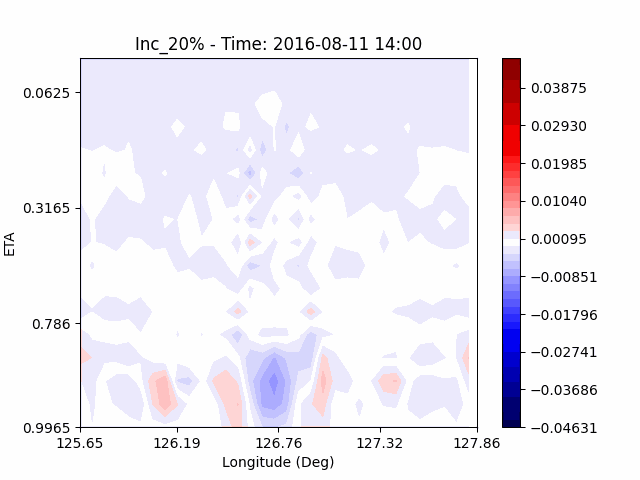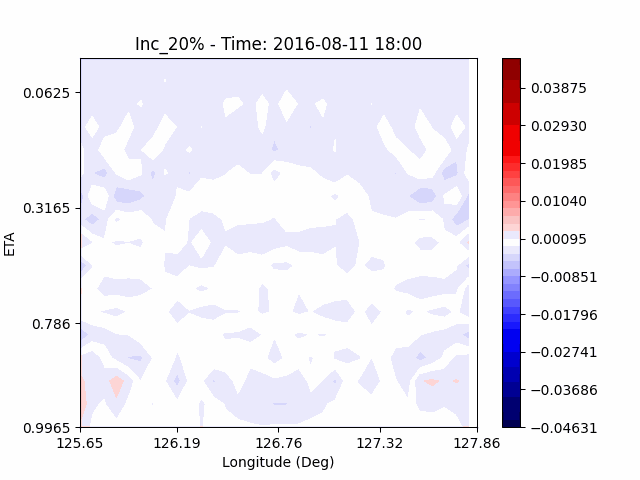
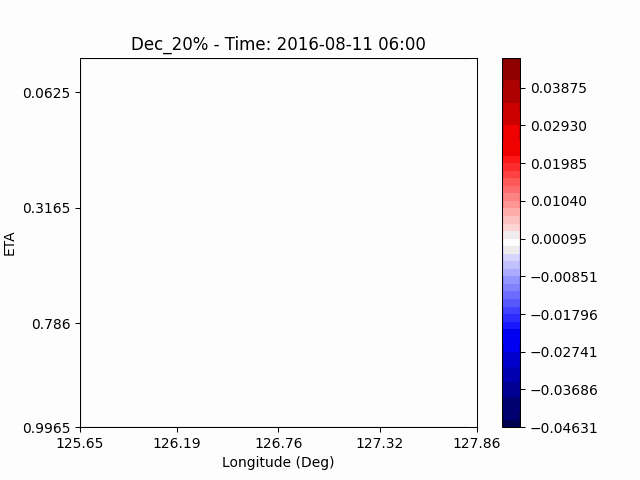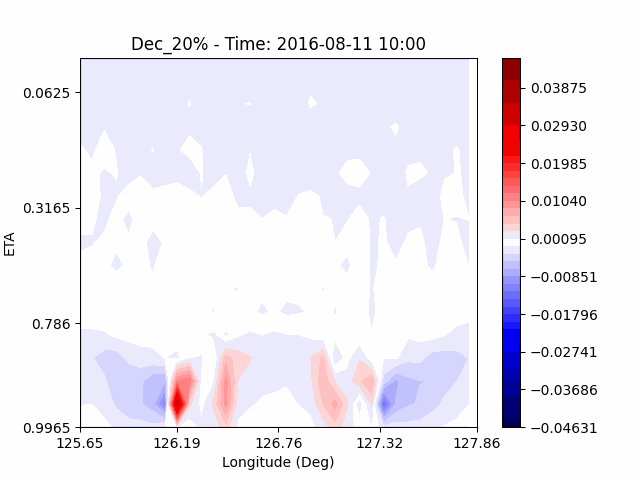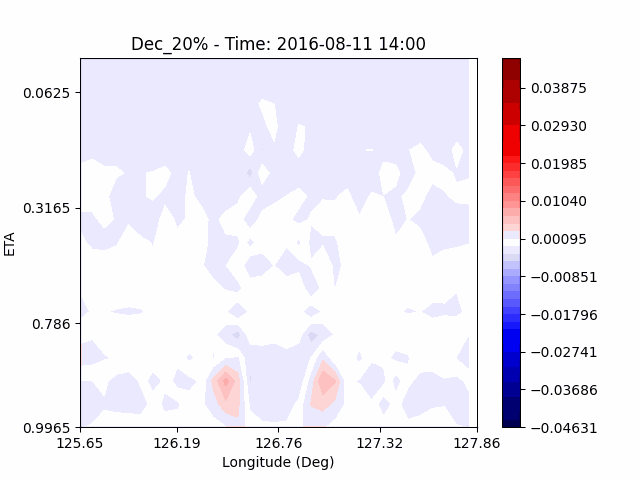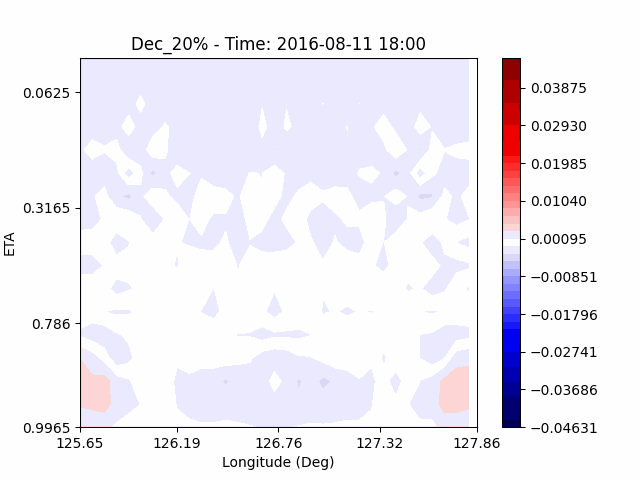

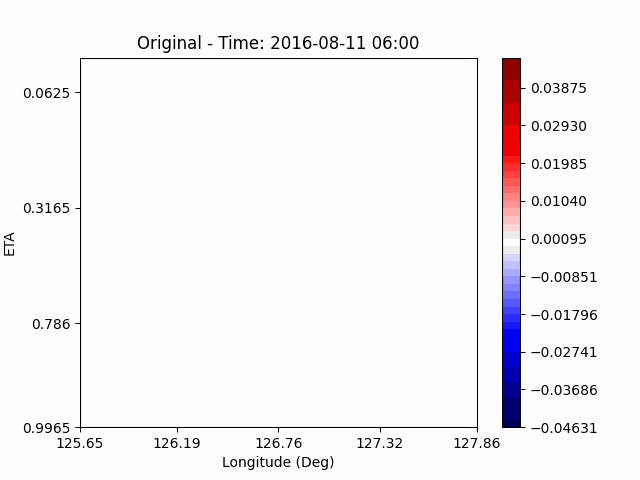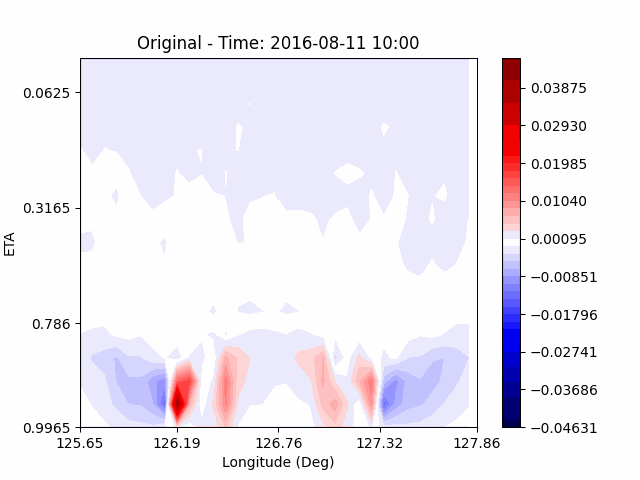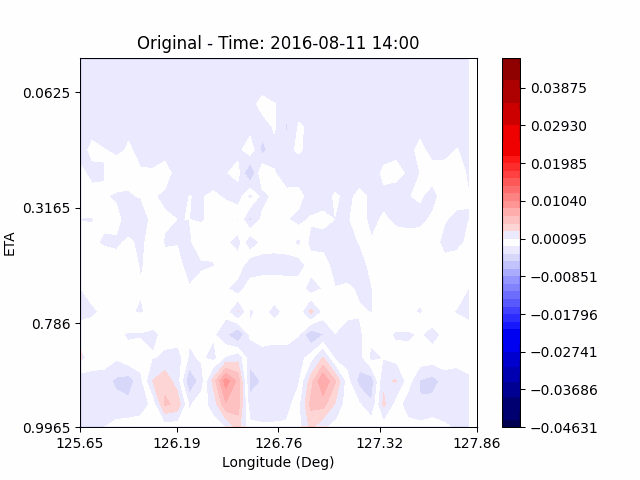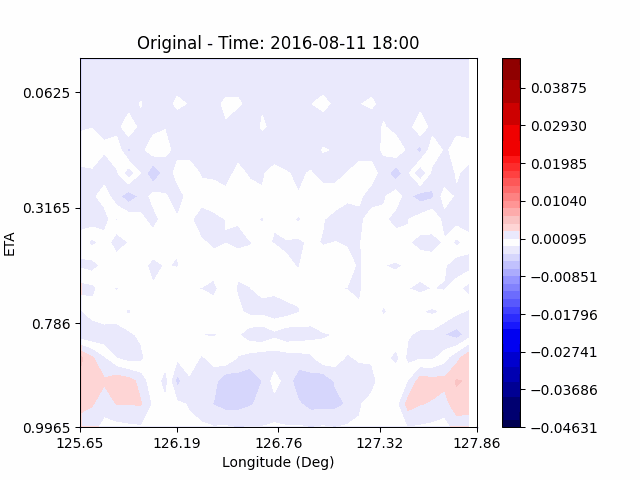
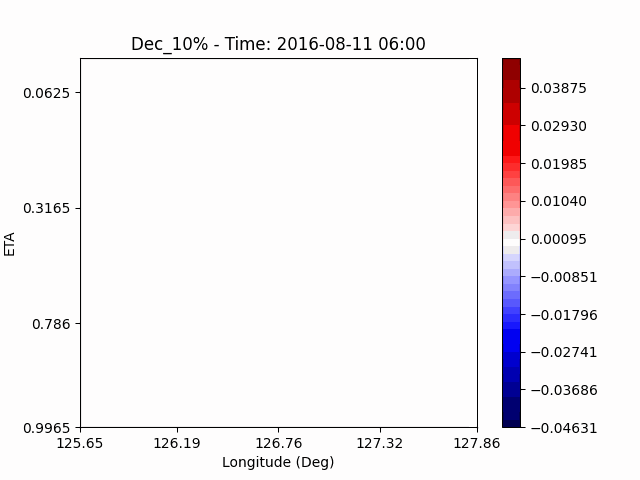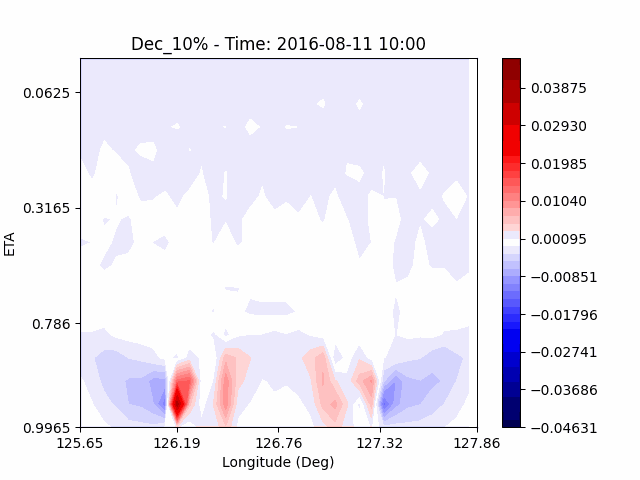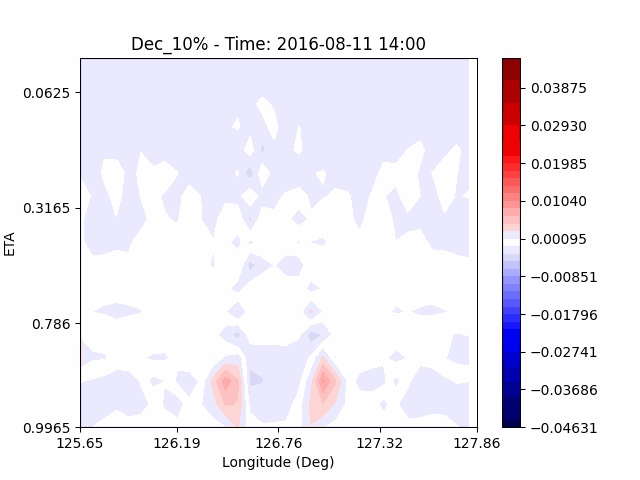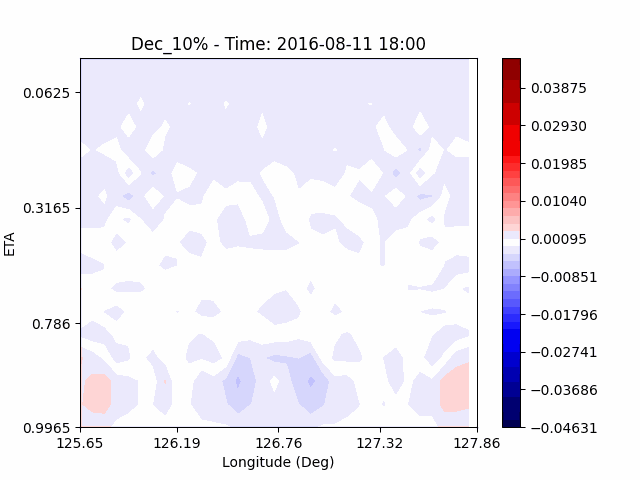
The w-directioal wind shows the position of the rising and falling winds changing with time. In the beginning, rising currents occur at the borders of the urban. The rising airflow gradually gathers and strengthens to the center of the city. After that, as the rising airflow gradually separates inside of the urban, we found that a strong downward flow formed in the center of the urban. And then the downward flow spread to the outer direction of the urban. From this, it was confirmed that if the air contains a lot of water vapor, the amount of heat that can contain water vapor increases, increasing the intensity of vertical convection of heat dome.
[Formation of the Urban Heat Dome Effect]





This is a diagram that expresses the process of forming urban heat islands using wind. At the beginning of creation, winds rise at the edge of the urban, and the rising winds gather around the middle of the urban by intensified u-directional winds. Then, when the upper u-directional wind weakens, the downward flow replaces the upward flow in the center of the urban because the convective cells are broken, and the downward airflow spreads from the center to the edge of the urban, compressing heat of the urban. We thought of this as the urban heat island effect. And from the wind analysis, we confirmed that if more water vapor is contained in the air, the intensity of the convection on urban heat dome increases.
